
An alternative test that can be used if you suspect that the data are drawn from non-normal distributions is the Mann-Whitney U test. Normality of the distributions can be tested using, for example, a Q-Q plot.
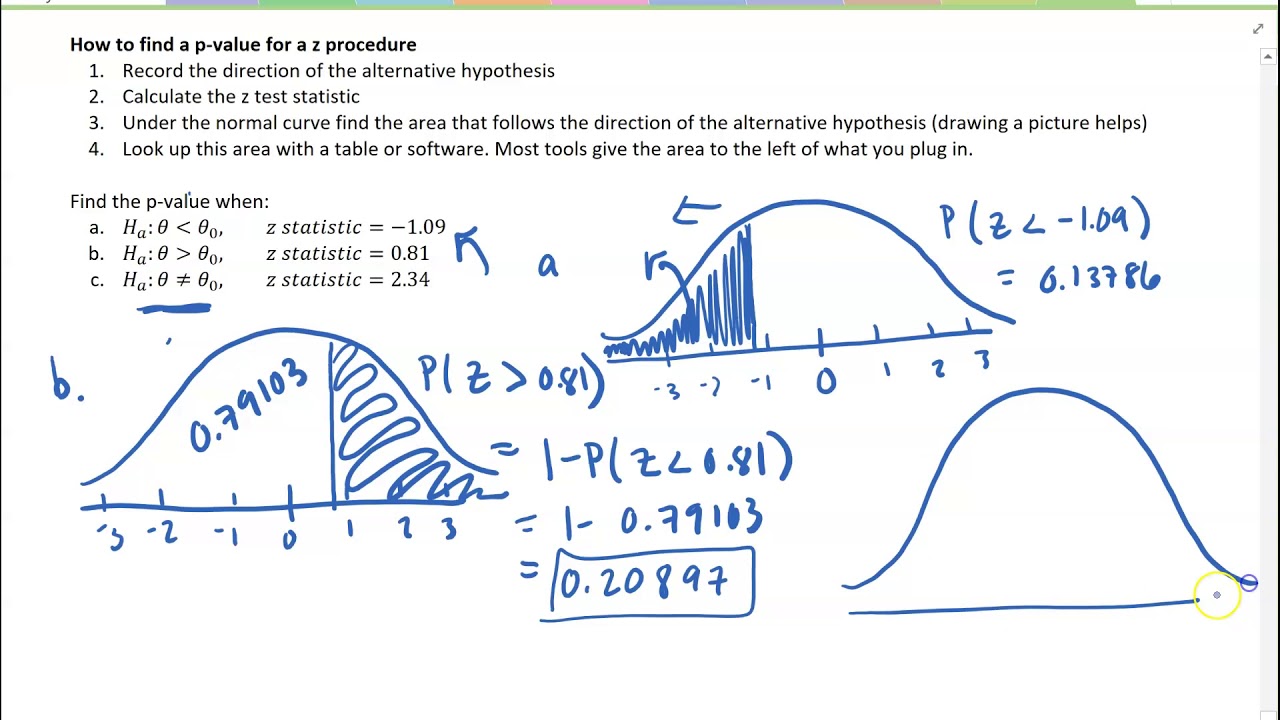
This test assumes that the two populations follow normal distributions (otherwise known as Gaussian distributions). Note that this result is not inconsistent with the previous result: with bigger samples we are able to detect smaller differences between populations.
If both sample sizes were increased to 20, the p-value would reduce to 0.048 (assuming the sample means and standard deviations remained the same), which we would interpret as strong evidence of a difference. Since this p-value is greater than 0.05, it would conventionally be interpreted as meaning that the data do not provide strong evidence of a difference in capillary density between individuals with and without ulcers. (All measurements are in capillaries per square mm.) Using this information, the p-value is calculated as 0.167. A control sample of 10 individuals without ulcers has mean capillary density of 34, with standard deviation 8.0. A sample of 10 patients with ulcers has mean capillary density of 29, with standard deviation 7.5. blood pressure of an individual before and after a drug is administered) then the appropriate test is the paired t-test.Ī study compares the average capillary density in the feet of individuals with and without ulcers. If you are comparing two measurements taken on the same sampling unit (e.g. the sampled individuals) in the two groups are independent. This calculator should be used when the sampling units (e.g. The most common choice of significance level is 0.05, but other values, such as 0.1 or 0.01 are also used. Typically a threshold (known as the significance level) is chosen, and a p-value less than the threshold is interpreted as indicating evidence of a difference between the population means. Therefore, the smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence is that the two populations have different means. The smaller the p-value, the more surprised we would be by the observed difference in sample means if there really was no difference between the population means. The p-value is the probability that the difference between the sample means is at least as large as what has been observed, under the assumption that the population means are equal.
It produces a “p-value”, which can be used to decide whether there is evidence of a difference between the two population means. This test is known as an a two sample (or unpaired) t-test. For example, based on blood pressures measurements taken from a sample of women and a sample of men, can we conclude that women and men have different mean blood pressures? Use this calculator to test whether samples from two independent populations provide evidence that the populations have different means.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
